What Is A Living Raw Food Diet?
A raw food diet consists of uncooked fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and sprouts. Raw foods are packed with intense nutrients, enzymes, and life force. When food is heated above 47°C (117°F), it loses valuable enzymes and vitamins, which play a crucial role in digestion and overall health. Since digestion relies on enzymes, the body must work harder to produce these lost enzymes to process cooked foods.
Cooked food is an inefficient way to fuel our bodies: it wastes energy and contributes to premature aging. Fortunately, our bodies are resilient and can rejuvenate if nourished properly. Eating raw, living foods helps the body cleanse itself, bringing about the healing of chronic conditions and a heightened sense of well-being.
Cooked foods are devoid of enzymes and lose many of their essential nutrients during the cooking process, which alters their molecular structure and may even render them toxic. Consuming too many overly cooked, processed, or microwaved foods can lead to digestive issues and contribute to conditions such as cancer, heart disease, diabetes, and other degenerative diseases. On the other hand, living foods, such as sprouted seeds and fresh sprouts, contain far more nutrients and enzymes than their cooked counterparts.
WHAT DO RAW / LIVING FOODISTS EAT?
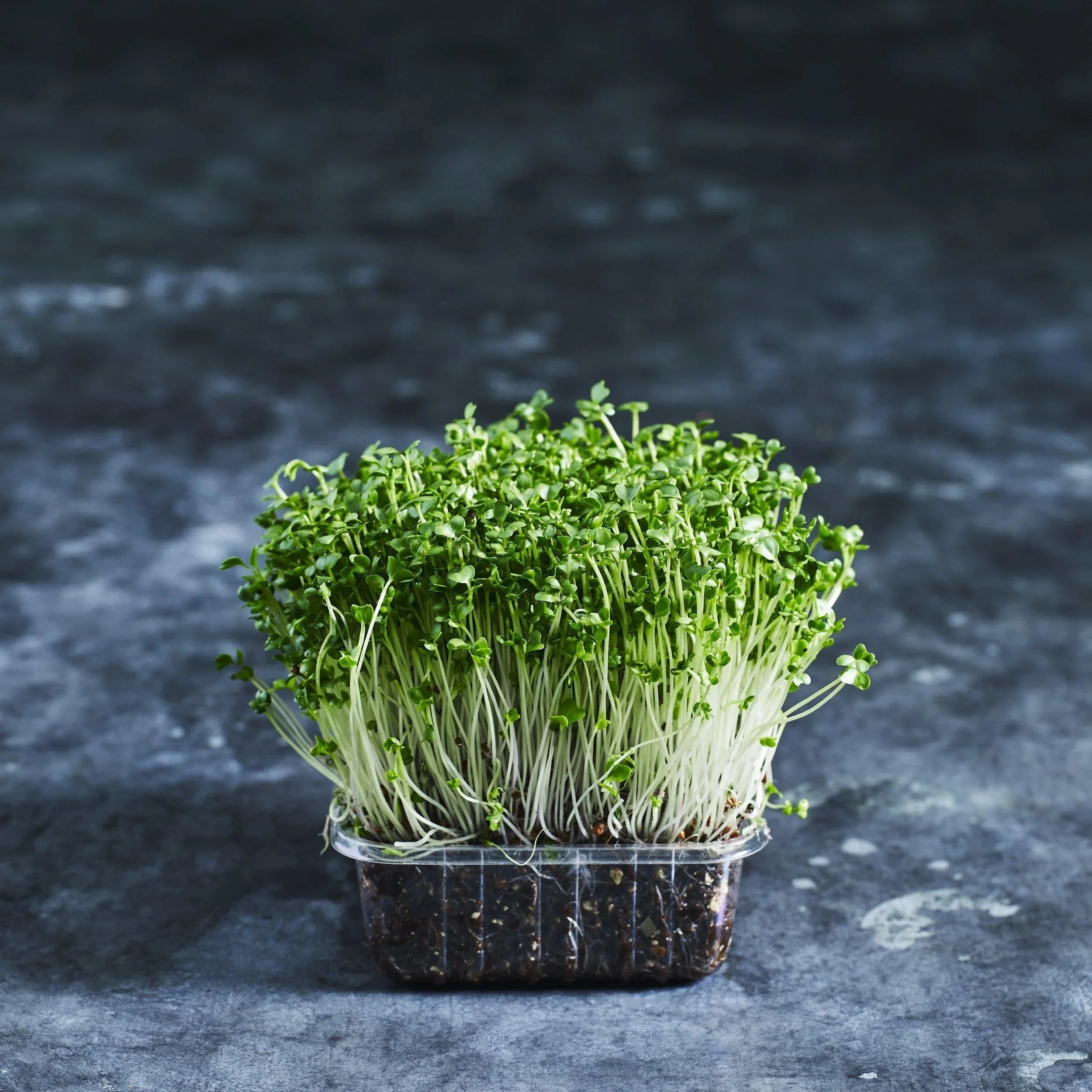
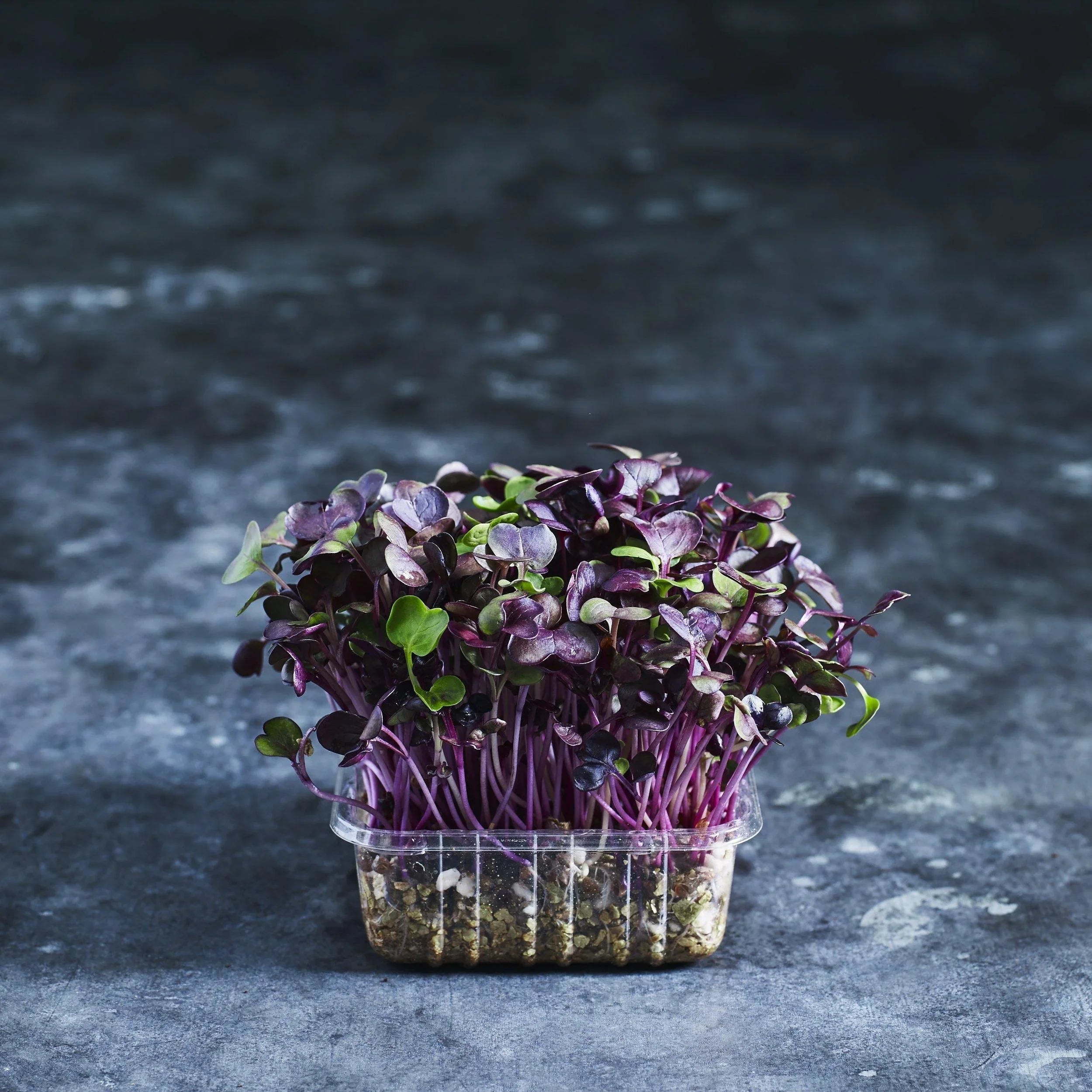
A raw food diet goes far beyond just apples and oranges. It includes a variety of fresh fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, sprouted legumes, sprouted grains (like wheatgrass and barley grass), algae, sea vegetables, herbs, spices, and fermented foods. Sprouts like broccoli sprouts, alfalfa sprouts, and radish sprouts are especially popular because they’re rich in enzymes and antioxidants, providing a dense nutrient profile in a small package.
The foundation of any raw food diet includes a wide range of fruits, vegetables, and greens. Other foods, like sprouted seeds and nuts, should make up only a small part of your daily menu. For example, sprouting sunflower seeds, pumpkin seeds, or lentils activates their enzymes, making them far easier to digest and boosting their nutritional value.
Processed foods, which are often pasteurized and loaded with additives, preservatives, salt, and sugar, should be avoided at all costs.
WHAT ARE ENZYMES?
Enzymes are the catalysts for every chemical reaction in our cells, enabling processes like digestion and immune function. These protein molecules are present in every cell of our body and are critical for our survival. Living foods, such as sprouts and sprouted seeds, are rich in active enzymes, which make them easier to digest and absorb compared to cooked foods.
Cooking destroys all enzymes in food. When you eat living foods like sprouted mung beans, alfalfa, or broccoli sprouts, you’re consuming enzymes that aid digestion. This means the body doesn’t need to expend as much energy producing its own enzymes, and instead, it can redirect that energy to healing, repairing, and rejuvenating.
THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN LIVING FOODS AND RAW FOODS
While both living and raw foods contain enzymes, living foods have a much higher enzyme content. Raw foods, such as unsprouted almonds or sunflower seeds, contain dormant enzymes. By soaking or sprouting them, you activate these enzymes, making the food much easier to digest and far more nutritious.
For example, if you soak and sprout lentils, they become living foods, and their nutritional profile is vastly improved. The sprouting process converts most of the starches into simple sugars and proteins, which are easier for the body to assimilate.
WHAT DO RAW FOODISTS DRINK?
Water is essential for hydration, as the body is made up of around 70% water. Beyond that, fresh fruit and vegetable juices are key components of a raw foodist’s diet. A good mix is 80% vegetables and 20% fruit, as this provides a balanced intake of nutrients without excess sugar.
Coconut water is another refreshing and hydrating option, packed with electrolytes, vitamins, and minerals. For those who enjoy herbal beverages, green tea and yerba mate are rich in antioxidants and vitamins, making them excellent choices for detoxification and immune support.
THE IMPORTANCE OF JUICING ON A RAW FOOD DIET
Juicing allows your body to absorb nutrients quickly, as it bypasses the need to digest fiber. It’s especially useful when consuming fiber-rich foods like kale, cabbage, or beetroot, which can be hard to break down with chewing alone. Juicing ensures the nutrients are absorbed efficiently into the bloodstream, promoting energy and vitality.
THE HEALTH BENEFITS OF EATING RAW FOODS
As you gradually transition to a raw food diet, you’ll likely notice increased energy, clearer skin, and improved digestion. A raw diet can help combat many chronic diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, and even cancer. It also slows the aging process and promotes a sense of well-being.
FOOD COMBINATION
When following a raw food diet, food combining is essential. Eating the wrong foods together can cause indigestion, bloating, and fatigue. For example, fruits, especially melons, are best eaten on an empty stomach, as they digest quickly. If combined with other foods that take longer to digest, such as nuts or vegetables, they can ferment in the stomach, leading to discomfort.
Soaked nuts and sprouted seeds like sunflower or pumpkin seeds can be combined with vegetables, while starchy carbohydrates like bananas, carrots, or pumpkins should not be paired with protein-rich foods such as nuts, seeds, or fermented foods like yogurt or cheese.
ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS
A well-balanced raw food diet provides all the essential nutrients your body needs, including vitamins, minerals, enzymes, antioxidants, healthy fats, and proteins. However, some nutrients may require extra attention, such as vitamin B12, vitamin A, omega-3 fatty acids, and zinc, which are sometimes low in a strictly plant-based raw food diet.
HOW TO GET STARTED
Transitioning to a 100% raw food diet may take time. Start by introducing one raw meal a day and gradually increase your raw food intake. Including nutrient-dense, sprouted foods like lentils, broccoli sprouts, and alfalfa sprouts will provide a solid foundation for your diet.
As you explore raw foods, don’t forget to include sprouted seeds like flax, chia, and hemp, which provide essential omega-3s and proteins. With the right preparation and a balanced approach, your body can undergo a transformation, feeling rejuvenated and full of energy.